Scientists led by a team from Fudan University in Shanghai have created a new flexible fiber chip as thin as a human hair. The development could usher...
Vous n'êtes pas connecté
- English
- Français
- عربي
- Español
- Deutsch
- Português
- русский язык
- Català
- Italiano
- Nederlands, Vlaams
- Norsk
- فارسی
- বাংলা
- اردو
- Azərbaycan dili
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Հայերեն
- Ελληνικά
- Bosanski jezik
- українська мова
- Íslenska
- Türkmen, Түркмен
- Türkçe
- Shqip
- Eesti keel
- magyar
- Қазақ тілі
- Kalaallisut ; kalaallit oqaasii
- Lietuvių kalba
- Latviešu valoda
- македонски јазик
- Монгол
- Bahasa Melayu ; بهاس ملايو
- ဗမာစာ
- Slovenščina
- тоҷикӣ ; toğikī ; تاجیکی
- ไทย
- O'zbek ; Ўзбек ; أۇزبېك
- Tiếng Việt
- ភាសាខ្មែរ
- རྫོང་ཁ
- Soomaaliga ; af Soomaali
 Maroc - KNOWRIDGE.COM - A La Une - 21/01/2025 14:16
Maroc - KNOWRIDGE.COM - A La Une - 21/01/2025 14:16
Chainmail-like material could revolutionize armor and tough materials
Scientists have created a groundbreaking new material inspired by chainmail, and it could change the future of armor. A research team led by Northwestern University has developed the first-ever two-dimensional (2D) mechanically interlocked material. This unique material is incredibly strong and flexible, making it ideal for lightweight body armor, durable fabrics, and other high-performance applications. […]
Articles similaires
Programmable Lego-Like Material Emulates Life’s Flexibility
Mechanical engineers at Duke University have demonstrated a proof-of-concept method for programming mechanical properties into solid Lego-like...
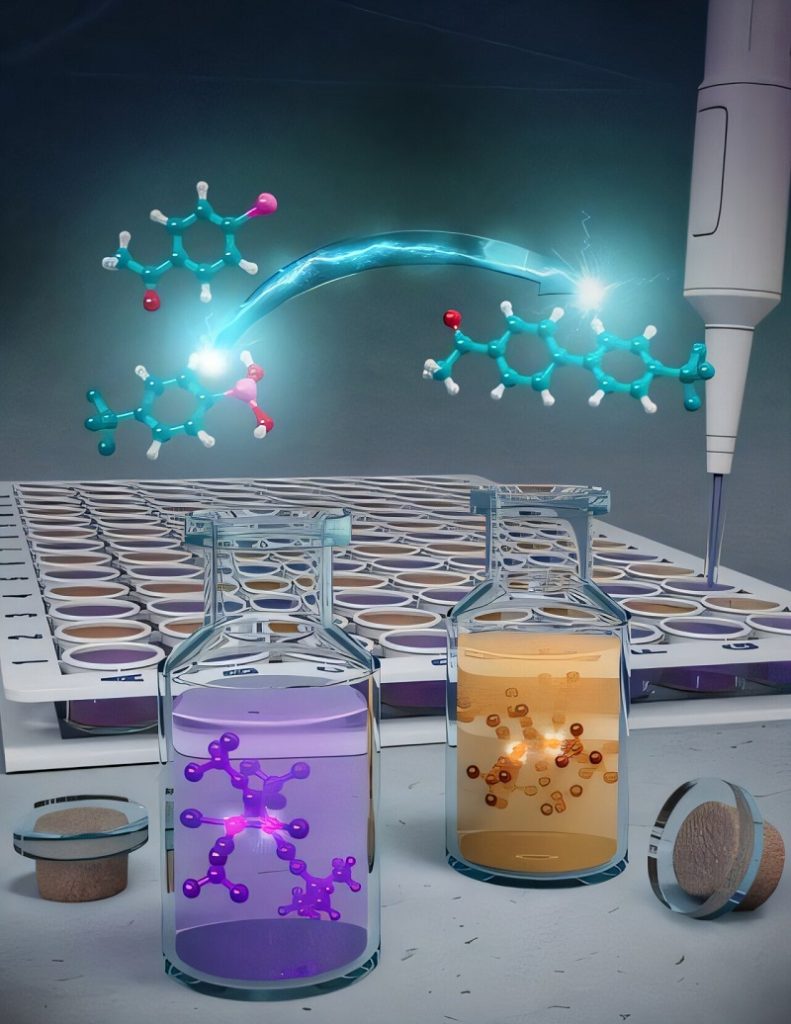
This nickel catalyst could change how drugs and materials are made
Chemists at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a new class of nickel catalysts that could significantly change how important...
This nickel catalyst could change how drugs and materials are made
Chemists at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a new class of nickel catalysts that could significantly change how important...
Take That review – could it be TV magic? Yes!
This fantastically enjoyable romp about the boy band covers the highs, the oiled thighs and the chainmail codpieces. But why does Gary Barlow...
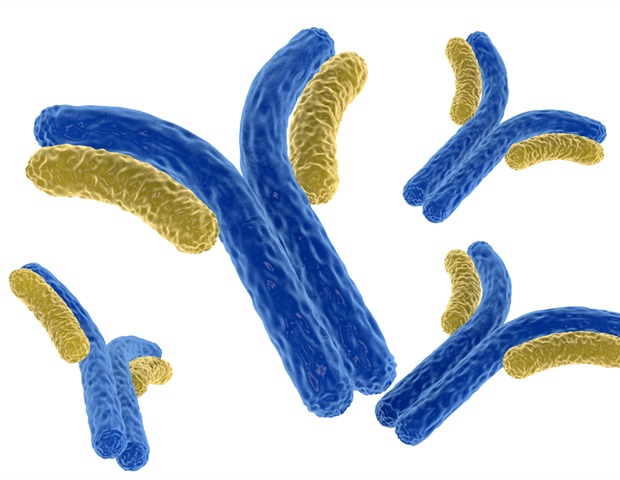
New platform improves prediction of human antibody drug responses
An international research consortium, led by scientists at VIB and UGent, has developed a new platform that could change how antibody medicines are...
Basil Zempilas 10 Things: Shambolic Labor decisions leave all West Australians worse off
West Australians are finding life incredibly tough, and with experts saying it could be as many as four interest rate rises over the next year - out...
Fungi turn shredded mattress foam into lightweight building insulation
Swinburne researchers have turned old, unwanted mattresses into safe and sustainable building insulation materials using fungi. The team grew a common...
Single-use test strip could revolutionize disease diagnosis
A research team led by La Trobe University has developed a single-use test strip which could ultimately change how diseases like cancer are diagnosed.
GeSn alloys emerge as a new semiconductor class that could reshape optoelectronics
Scientists have created a new type of material that could enable common electronic devices to work faster and use less energy, a study suggests. The...
Les derniers communiqués
-
Evergreen Elevate Heads to Australia to Empower MSPs with Valuable Strategies and Insights on Better M&A Practices
Evergreen Elevate - 29/07/2025