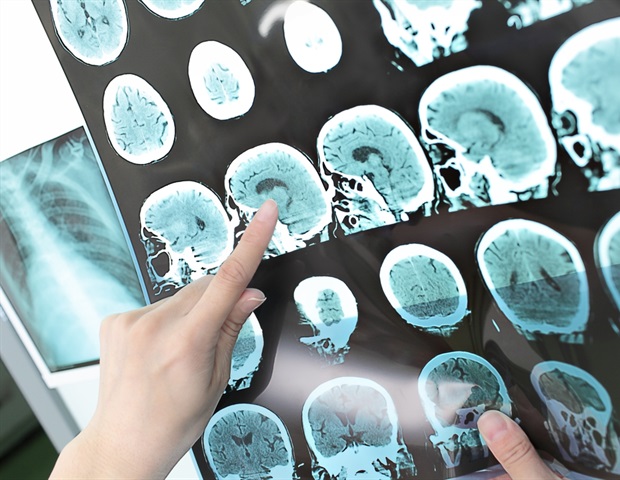
Removing a blood clot from a major brain artery and injecting the clot-dissolving drug btenecteplase/b significantly improves medlinkstroke/medlink
Vous n'êtes pas connecté
- English
- Français
- عربي
- Español
- Deutsch
- Português
- русский язык
- Català
- Italiano
- Nederlands, Vlaams
- Norsk
- فارسی
- বাংলা
- اردو
- Azərbaycan dili
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Հայերեն
- Ελληνικά
- Bosanski jezik
- українська мова
- Íslenska
- Türkmen, Түркмен
- Türkçe
- Shqip
- Eesti keel
- magyar
- Қазақ тілі
- Kalaallisut ; kalaallit oqaasii
- Lietuvių kalba
- Latviešu valoda
- македонски јазик
- Монгол
- Bahasa Melayu ; بهاس ملايو
- ဗမာစာ
- Slovenščina
- тоҷикӣ ; toğikī ; تاجیکی
- ไทย
- O'zbek ; Ўзбек ; أۇزبېك
- Tiếng Việt
- ភាសាខ្មែរ
- རྫོང་ཁ
- Soomaaliga ; af Soomaali
 Maroc - NEWS.MEDICAL.NET - A la Une - 09/Feb 03:22
Maroc - NEWS.MEDICAL.NET - A la Une - 09/Feb 03:22
Tenecteplase injection after clot removal improves stroke recovery
Removing a blood clot from a large brain artery, then injecting the clot-dissolving drug tenecteplase into the artery resulted in stroke survivors being more likely to have better function 90 days after their stroke than those receiving standard clot removal, according to preliminary late-breaking science presented today at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2025.
Articles similaires
Combining Clot Removal With Clot-Buster Shot Could Improve Stroke Recovery
Injecting tenecteplase into the artery after clot removal helps improve recovery in stroke survivors, leading to better functional outcomes.
Clot-busting drug alteplase shows promise for stroke treatment up to 24 hours after onset
The clot-dissolving medication, alteplase, improved stroke patients' recovery by more than 50% when given up to 24 hours after the beginning of an...
This drug could treat stroke beyond standard time window
A new study has found that the clot-dissolving drug alteplase can significantly improve stroke recovery even when given up to 24 hours after a stroke...
Alteplase May Improve Stroke Recovery Up to 24 Hours After Symptoms
Recent study presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2025 suggests that the clot-dissolving medication...
This blood pressure drug may lower stroke risk in women with migraine headaches
A common blood pressure medication used to prevent migraines may also significantly reduce the risk of ischemic stroke in women, according to a new...
Shorter telomeres linked to higher risk of stroke, dementia, and depression
A new study suggests that people with shorter protective caps at the ends of their chromosomes, called telomeres, may have a higher risk of...
How strokes affect older people in the long run
A stroke is a serious medical event that can change a person’s life in many ways, especially for older adults. It happens when blood flow to the...
Alteplase May Improve Stroke Recovery Up to 24 Hours After Symptoms
Alteplase improves stroke recovery by over 50% when given up to 24 hours after symptom onset, offering hope for patients with delayed access to...
Les derniers communiqués
-
Aucun élément