Our bodies rely on tiny structures called mitochondria to generate energy for our cells. These structures are often described as the “powerhouses”...
Vous n'êtes pas connecté
- English
- Français
- عربي
- Español
- Deutsch
- Português
- русский язык
- Català
- Italiano
- Nederlands, Vlaams
- Norsk
- فارسی
- বাংলা
- اردو
- Azərbaycan dili
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Հայերեն
- Ελληνικά
- Bosanski jezik
- українська мова
- Íslenska
- Türkmen, Түркмен
- Türkçe
- Shqip
- Eesti keel
- magyar
- Қазақ тілі
- Kalaallisut ; kalaallit oqaasii
- Lietuvių kalba
- Latviešu valoda
- македонски јазик
- Монгол
- Bahasa Melayu ; بهاس ملايو
- ဗမာစာ
- Slovenščina
- тоҷикӣ ; toğikī ; تاجیکی
- ไทย
- O'zbek ; Ўзбек ; أۇزبېك
- Tiếng Việt
- ភាសាខ្មែរ
- རྫོང་ཁ
- Soomaaliga ; af Soomaali
 Maroc - KNOWRIDGE.COM - A La Une - 09/Feb 11:00
Maroc - KNOWRIDGE.COM - A La Une - 09/Feb 11:00
Scientists find a new way to fight inflammation
Mitochondria, often called the powerhouses of the cell, do more than produce energy. A recent study published in Science Advances by researchers in Navdeep Chandel’s lab at Northwestern University reveals that mitochondria play a key role in regulating the immune system and controlling inflammation. These findings open the door to new therapies for inflammatory diseases like inflammatory […] The post Scientists find a new way to fight inflammation appeared first on Knowridge Science Report.
Articles similaires
A way to cut Diabetes
Mitochondrial damage is common in metabolic diseases like Diabetes, affecting insulin production and function in patients. Diabetics’...
Trending Discoveries in Laboratory Science: Paving the Way for Innovation
Laboratory science is at the forefront of groundbreakingdiscoveries, pushing the boundaries of knowledge and transforming industries ranging from...
Research highlights gender and age differences in eye gene therapy responses
Older women could be vulnerable to harmful inflammation from new gene therapies to treat incurable eye diseases, new research has found.
New findings could make off-the-shelf CAR T cell therapy a reality
CAR T cell therapy is one of the most promising new cancer treatments to emerge in recent years. It involves removing a patient's own immune T cells...
Scientists unlock new way to build stronger, smarter materials with 3D printing
Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have made an exciting breakthrough in multi-material 3D printing by using capillary...
New lab-on-chip platform to revolutionize cancer diagnosis by expediting tumour cell detection
Cancer remains one of the world’s deadliest diseases, responsible for nearly 10 million deaths in 2020 alone, according to the World Health...
Scientists create highly conductive 2D polymer, paving the way for advanced electronics
A team of international researchers has successfully created a new type of highly conductive 2D polymer, opening the door to exciting new applications...
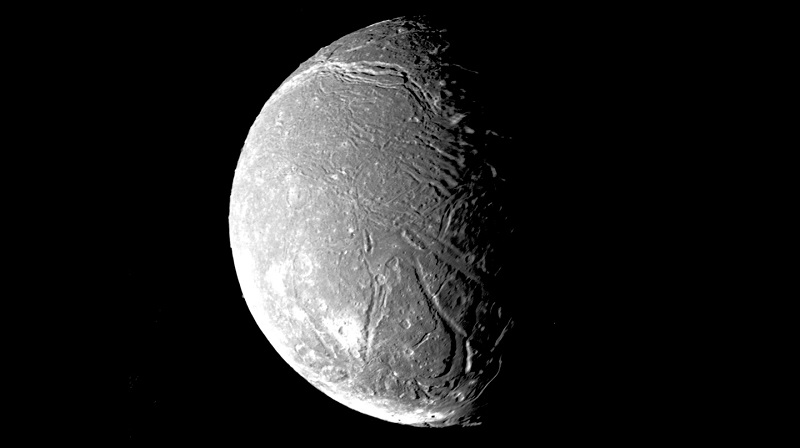
Mysterious trenches on Uranus’ moon ariel may reveal its hidden secrets
Scientists have discovered that deep trenches on Uranus’ moon Ariel might be pathways for material from its interior to reach the surface. These...
Brain's Immune Gatekeepers: How Tregs Protect Memory and Health
Can immune cells protect your brain? Yes! Tregs act as gatekeepers, controlling inflammation and supporting memory formation in the hippocampus.
Les derniers communiqués
-
Aucun élément