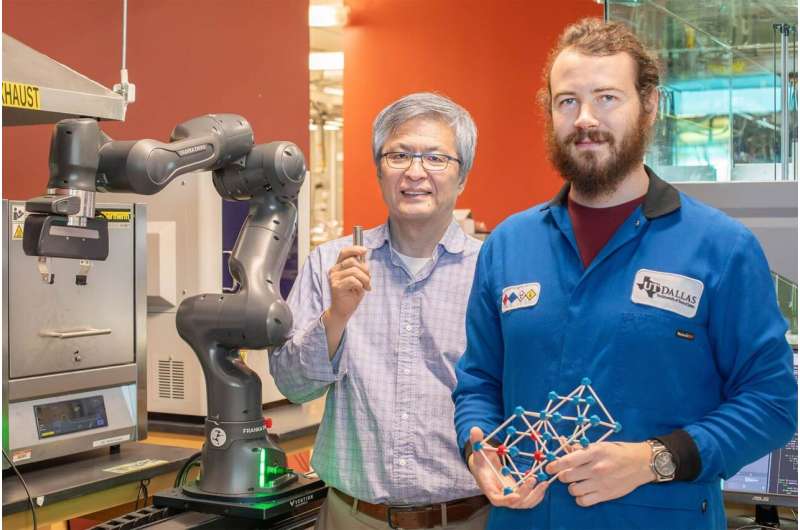
Lithium nickel oxide (LiNiO₂) has shown great potential for powering the next generation of lithium-ion batteries, promising longer battery...
Vous n'êtes pas connecté
- English
- Français
- عربي
- Español
- Deutsch
- Português
- русский язык
- Català
- Italiano
- Nederlands, Vlaams
- Norsk
- فارسی
- বাংলা
- اردو
- Azərbaycan dili
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Հայերեն
- Ελληνικά
- Bosanski jezik
- українська мова
- Íslenska
- Türkmen, Түркмен
- Türkçe
- Shqip
- Eesti keel
- magyar
- Қазақ тілі
- Kalaallisut ; kalaallit oqaasii
- Lietuvių kalba
- Latviešu valoda
- македонски јазик
- Монгол
- Bahasa Melayu ; بهاس ملايو
- ဗမာစာ
- Slovenščina
- тоҷикӣ ; toğikī ; تاجیکی
- ไทย
- O'zbek ; Ўзбек ; أۇزبېك
- Tiếng Việt
- ភាសាខ្មែរ
- རྫོང་ཁ
- Soomaaliga ; af Soomaali
Rubriques :
 Maroc - TECHXPLORE.COM - RSS news feed - Hier 11:30
Maroc - TECHXPLORE.COM - RSS news feed - Hier 11:30
Asymmetric ether solvents enhance Li-metal battery charging and stability
To fuel the future advancement of the electronics industry, engineers will need to develop batteries that can be charged quickly, have higher energy densities (i.e., can store more energy) and last longer. Among the most promising alternatives to lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, which power most devices on the market today, are lithium-metal batteries (LMBs).
Articles similaires
High-performance sodium-ion cathode paves the way for lithium-ion battery alternative
For decades, scientists have sought ways to counter our dependence on lithium-ion batteries. These traditional, rechargeable batteries energize...
Anode-free solid-state batteries: Fundamental insights bring them a step closer to practical use
From laptops to electric vehicles, lithium-ion batteries power everyday life. However, as demand for longer-lasting devices threatens to outstrip the...
Tin foam powers new battery electrode innovation
Tin can be processed into a highly porous foam. An interdisciplinary team at HZB has investigated how this tin foam (pictured) behaves as a battery...
Will Lamborghini use sodium-ion batteries for its first EV?
While one would expect a luxury carmaker like Lamborghini to bet on solid-state technology for its debut in the electric supercar market, the Italian...
Tin foam powers new battery electrode innovation
Metal-based electrodes in lithium-ion batteries promise significantly higher capacities than conventional graphite electrodes. Unfortunately, they...
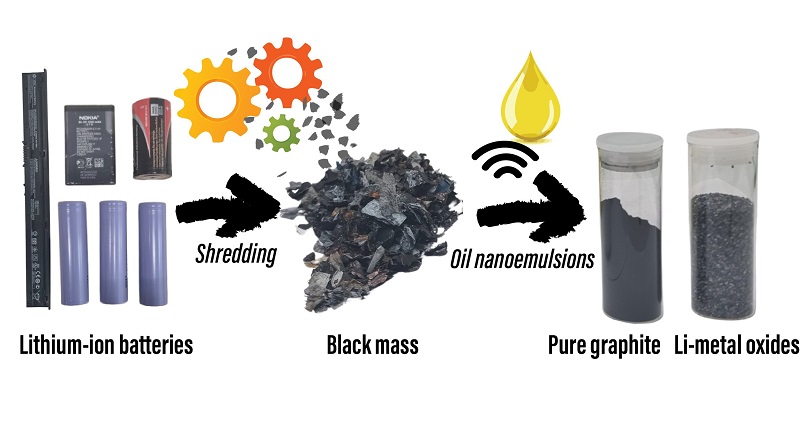
Scientists discover a green way to recycle lithium-ion batteries using cooking oil
Scientists at the University of Leicester have developed a new, eco-friendly way to recycle lithium-ion batteries using a simple mix of water and...
ARENA backs new battery cathode technology
Image: Chor muang/stock.adobe.com The Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) will provide $30 million to support the commercialisation of a new...
Rejuvenating lithium-ion batteries by injecting them with a widely compatible carrier molecule
A multi-institutional team of Chinese chemists, molecular engineers, and materials scientists has found a way to rejuvenate lithium-ion batteries...
Boosting seawater battery performance with wood waste-derived catalysts
Seawater batteries represent the next generation of energy storage devices, capable of efficiently storing and discharging electricity derived from...
Les derniers communiqués
-
Adobe Brings Conversational AI to Trillions of PDFs with the New AI Assistant in Reader and Acrobat
Adobe - 21/02/2024
-
Laura Frigenti takes the Helm as Chief Executive Officer of the Global Partnership for Education
Global Partnership for Education - 05/12/2022